1. Implement strStr() Function in String
Given two strings needle and haystack, return the index of the first occurrence of needle in haystack, or -1 if needle is not part of haystack.
Clarification:
What should we return when needle is an empty string? This is a great question to ask during an interview.
For the purpose of this problem, we will return 0 when needle is an empty string. This is consistent to C's strstr() and Java's indexOf().
Example 1:
Input: haystack = "hello", needle = "ll" Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: haystack = "aaaaa", needle = "bba" Output: -1
Constraints:
- 1 <= haystack.length, needle.length <= 104
- haystack and needle consist of only lowercase English characters.
2. Cheapest Flights Within K Stops
There are n cities connected by some number of flights. You are given an array flights where flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei] indicates that there is a flight from city fromi to city toi with cost pricei.
You are also given three integers src, dst, and k, return the cheapest price from src to dst with at most k stops. If there is no such route, return -1.
Example 1:
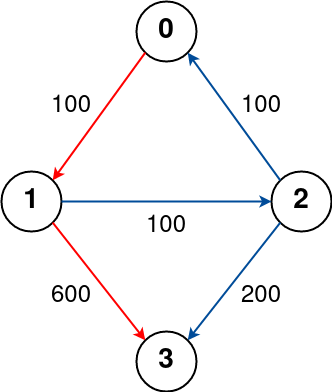
Input: n = 4, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[2,0,100],[1,3,600],[2,3,200]], src = 0, dst = 3, k = 1 Output: 700 Explanation: The graph is shown above. The optimal path with at most 1 stop from city 0 to 3 is marked in red and has cost 100 + 600 = 700. Note that the path through cities [0,1,2,3] is cheaper but is invalid because it uses 2 stops.
Example 2:
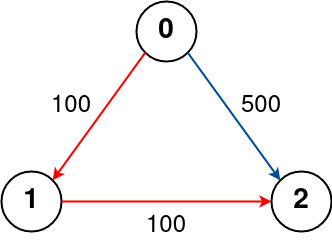
Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1 Output: 200 Explanation: The graph is shown above. The optimal path with at most 1 stop from city 0 to 2 is marked in red and has cost 100 + 100 = 200.
Example 3:
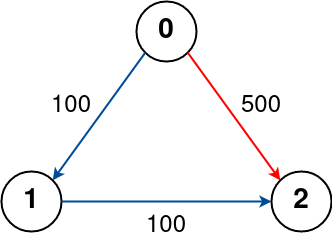
Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 0 Output: 500 Explanation: The graph is shown above. The optimal path with no stops from city 0 to 2 is marked in red and has cost 500.
Constraints:
- 1 <= n <= 100
- 0 <= flights.length <= (n * (n - 1) / 2)
- flights[i].length == 3
- 0 <= fromi, toi < n
- fromi != toi
- 1 <= pricei <= 104
- There will not be any multiple flights between two cities.
- 0 <= src, dst, k < n
- src != dst
3. "Shortest Path to Acquire All Keys in a Grid"
You are given an m x n grid grid where:
- '.' is an empty cell.
- '#' is a wall.
- '@' is the starting point.
- Lowercase letters represent keys.
- Uppercase letters represent locks.
You start at the starting point and one move consists of walking one space in one of the four cardinal directions. You cannot walk outside the grid, or walk into a wall.
If you walk over a key, you can pick it up and you cannot walk over a lock unless you have its corresponding key.
For some 1 <= k <= 6, there is exactly one lowercase and one uppercase letter of the first k letters of the English alphabet in the grid. This means that there is exactly one key for each lock, and one lock for each key; and also that the letters used to represent the keys and locks were chosen in the same order as the English alphabet.
Return the lowest number of moves to acquire all keys. If it is impossible, return -1.
Example 1:
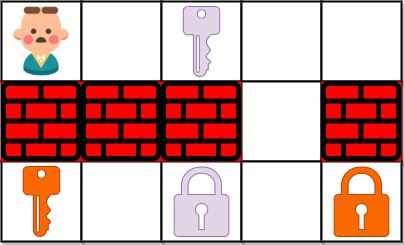
Input: grid = ["@.a..","###.#","b.A.B"] Output: 8 Explanation: Note that the goal is to obtain all the keys not to open all the locks.
Example 2:
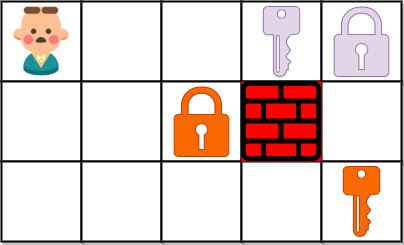
Input: grid = ["@..aA","..B#.","....b"] Output: 6
Example 3:

Input: grid = ["@Aa"] Output: -1
Constraints:
- m == grid.length
- n == grid[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 30
- grid[i][j] is either an English letter, '.', '#', or '@'.
- The number of keys in the grid is in the range [1, 6].
- Each key in the grid is unique.
- Each key in the grid has a matching lock.
4. Min number of donuts in unit time
给定每个时间单位最多生产多少个甜甜圈 vector<int> numOfDonuts,以及最多使用多长时间吃完所有的甜甜圈 maxTime,求每个时间单位最少吃的甜甜圈个数 d。
5. Max intereste level from non overlapping experiences
Airbnb has an "Experiences" product where you choose activities to do with your friends.
Each activity has a start time, end time, and interest level.
If you are given a list of potential "experiences",
Write a method that returns the maximum interest_level if you chose
non-overlapping experiences
[start_time, end_time, interest_level]
experiences = [(2, 5, 5),(3, 6, 6),(5, 10, 2),(4, 10, 8),(8, 9, 5),(13, 14, 1),(13, 17, 5),(14, 16, 8) ]
the answer should be 20
(3, 6, 6) (8, 9, 5) (13, 14, 1) (14, 16, 8)
Each activity has a start time, end time, and interest level.
If you are given a list of potential "experiences",
Write a method that returns the maximum interest_level if you chose
non-overlapping experiences
[start_time, end_time, interest_level]
experiences = [(2, 5, 5),(3, 6, 6),(5, 10, 2),(4, 10, 8),(8, 9, 5),(13, 14, 1),(13, 17, 5),(14, 16, 8) ]
the answer should be 20
(3, 6, 6) (8, 9, 5) (13, 14, 1) (14, 16, 8)